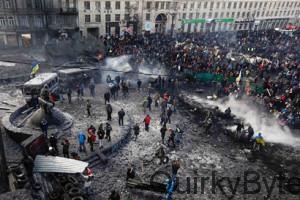Eastern Promises: Ukraine Crisis
It all began on 21st November, 2013, when Ukrainian president Viktor Yanukovych suspended any and all preparations for Ukraine joining the European Union which resulted in a widespread protest, Although, purely domestic at first, the protest spiraled into a revolt of the masses against the government resulting ousting of President Viktor Yanukovych by a revolution in February 2014 including riot police and armed citizens. This immediate series of changes in Ukraine’s sociopolitical system left the country with an interim government, an ongoing internal conflict and all severed ties with the European union.
Instead of the EU, the new government chose to align itself with the Russia seeking incentives of $15 billion in loans, cheaper gas prices and a geographically close trade partner, this, of course, upset the west and the already bad EU-Russia conflicts were once again, fueled by this.
Due to this, Ukraine had the eyes of the world upon it, Russia had convinced a to-be member of the EU to align with it upsetting the EU, the NATO, The US all at once.
The conflict did not settle with the changing of government and Ukraine’s alignment with Russia, protesters were now divided, Pro-Russians and anti-revolution activists clashed with each other on numerous occasions and the internal conflict in Ukraine was prolonged even longer, this time, between its own citizens separated by ideologies.
The world was gripped in fear of an armed conflict when Russian forces annexed the peninsular region of Crimea in Ukraine stating that it had to be done to protect the ethnically Russian population in that region, The chances of an armed conflict between the Ukrainian army, the NATO, The United States of America and Russia were as high as the cold war.
Armed conflict aside, the geopolitics of the European region was changed when conflicts in the form of sanctions were placed on all countries involved, On 6 March 2014, US president Barack Obama, invoking the International Emergency Economic Powers Act and the National Emergencies Act, signed an executive order that declared a national emergency and ordered sanctions, including travel bans and freezing of their U.S. assets to and in Russia. On 19 March, Australia imposed sanctions on Russia after the annexation of Crimea from Ukraine. The Australian government imposed targeted financial sanctions and travel bans on those who have been instrumental in the Russian threat to Ukraine’s sovereignty.
The ongoing financial crisis in Russia and the associated shrinking of the Russian economy is the partly the result of the all the sanctions against Russia Any international aid to Russia is considered unlikely as a result of the 2014–15 Russian military intervention in Ukraine,Moreover the United States and the European Union will not ease economic sanctions imposed on Russia due to Russia’s annexation of Crimea and Russian assistance to separatists militants fighting Ukraine in the conflicts.
Economic sanctions have also to the decline of the ruble since Russian companies have been prevented from rolling over debt, forcing companies to exchange their rubles for U.S. dollars or other foreign currencies on the open market to meet their interest payment obligations on their existing debt. The U.S. believes the sanctions have negatively affected the Russian economy so far and would continue to do so.