NASA Gives New Constellations Their Names After The Incredible Hulk And Thor’s Hammer

The Incredible Hulk And Thor’s Hammer:
The generation that is growing up now could consider themselves very lucky as they are in an era where Superheroes are getting all kinds of priorities in the entertainment section. Hollywood has gotten extremely Superhero dominant.
Comic book sales are on an all-time high and TV started focusing massively upon Superhero shows. So if people do want everything to be based on these fictional lovable characters, then why Science should be left behind?
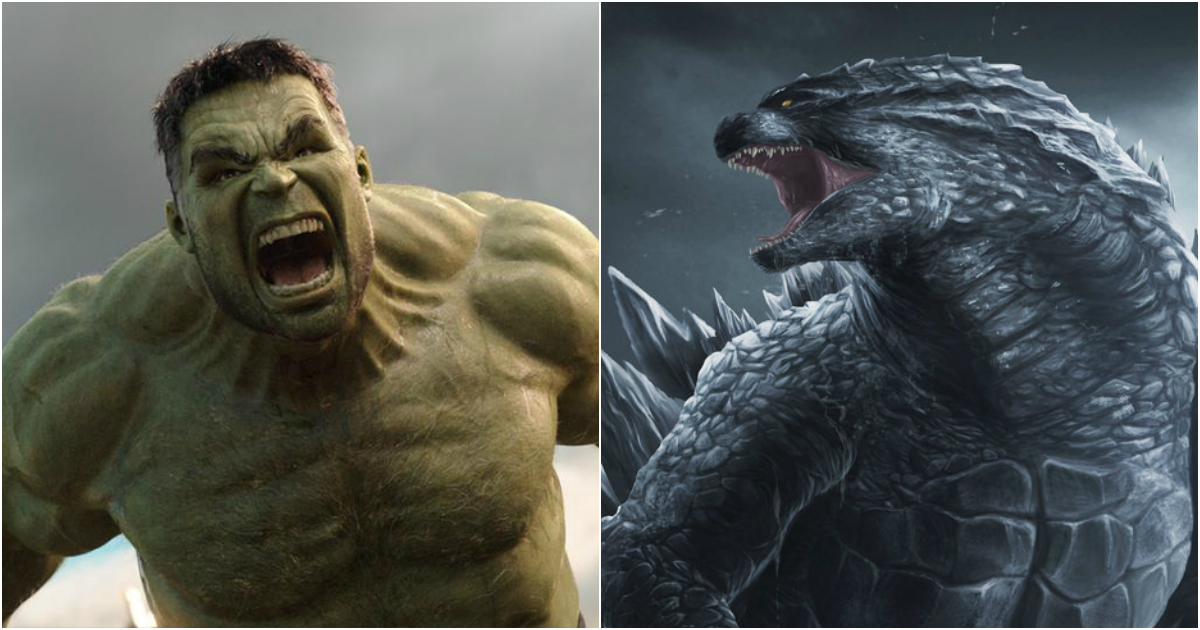
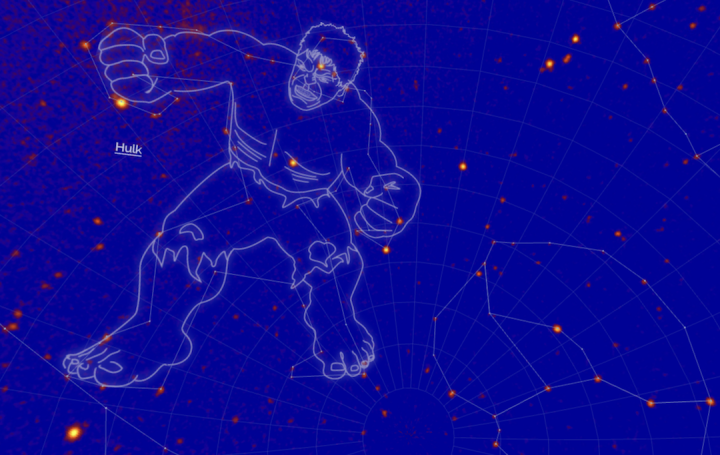
NASA Scientists recently named a new Constellation after Godzilla, and now Marvel also seems to be getting their recognition as they have named another newly discovered constellation after The Incredible Hulk. The reasoning for this naming is a bit funny, but we will take it!
The name is not just fancy and catchy, but the facts of discovery are actually similar to the origin of the Incredible Hulk. Banner transformed into the Hulk as he was exposed to the explosion of a gamma-ray bomb, and these new constellations are not actually based on star clusters, but rather gamma rays that were observed by the Fermi telescope. So, that’s a bit of inside joke for everyone.
Here’s the statement that they gave up on the announcement:
“Comic book fans all know the backstory of Hulk, the big, green, angry alter ego of Dr. Bruce Banner, whose experiments with gamma rays went terribly wrong. Gamma rays are the strongest form of light. They pack enough punch to convert into matter under the right circumstances, a transformation both Banner and the Hulk would certainly appreciate.”
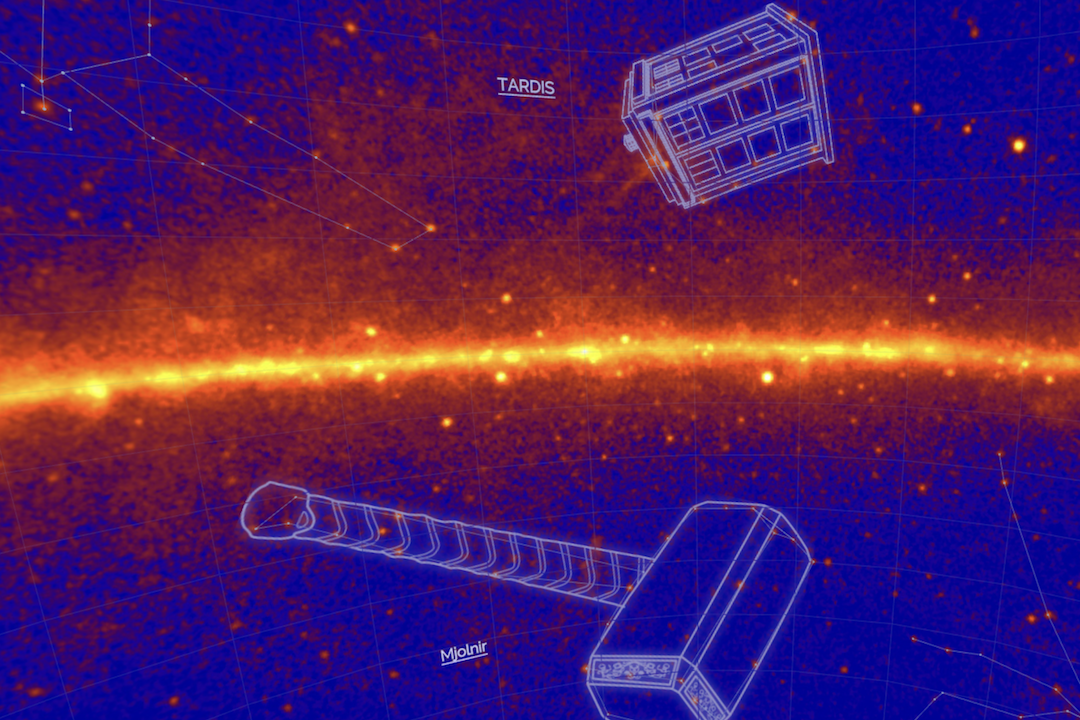
Apart from these two new constellations, there are several new gamma-ray constellations which have gotten their names after many pop culture references.
There’s a reference to the Doctor Who franchise (“Tardis”) and Thor’s hammer (“Mjolnir“), and if you are really interested in finding out some more info, NASA has a full breakdown of 21 new constellations along with their pictures that demonstrate their names after certain characters. You can read that here.
Here’s the rest of the statement made by NASA upon announcing the names of the new Constellations:
“All light carries energy. Visible light provides enough energy that solar panels can convert it into electricity, and green plants use it to manufacture food. Higher-energy ultraviolet light can give us suntans and sunburns. At still higher energies, X-rays can penetrate materials, allowing doctors to see broken bones and airport security personnel to check baggage.
The lowest-energy gamma rays seen by Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT) carry more than 6 million times the energy of the bluest visible light. At the high end, the LAT is designed to detect gamma rays with energies tens of millions of times greater than this.
The LAT works by taking advantage of the ability of gamma rays to transform into matter. The instrument contains dense foils of tungsten. When a gamma ray enters the LAT, it travels through these foils until it passes close to a tungsten atom. The interaction transforms the gamma ray into an electron and its antimatter counterpart, a positron. These particles continue through the LAT, which tracks them to figure out the direction of the original gamma ray.
Scientists call this process pair production. The reverse process, called pair annihilation, occurs when an electron collides with a positron, resulting in a gamma ray. In an unusual episode in 2009, a thunderstorm shot a beam of positrons (antimatter) into space and the particles struck Fermi. When the particles collided with electrons in the spacecraft, they annihilated in a flash of gamma rays. For a moment, Fermi became a source of gamma rays, and its instruments detected the glow.
Fermi sees gamma rays from sources as diverse as thunderstorms on Earth, stellar explosions across the universe, pulsars in our own and other galaxies, and distant galaxies where supermassive black holes power especially intense emissions. In fact, these galaxies make up more than half the high-energy sources Fermi has cataloged in the sky to date. By studying the strongest form of light, scientists are able to access extraordinary astrophysical environments and gain insight into the extreme processes occurring within them.”
Pop culture references are always welcome, so keep up the good work NASA. We certainly need more of these in the future!